vue源码分析(五) 静态属性和方法
# 1. 概述
在上一章——vue源码分析(四) 实例属性和方法 (opens new window),中我们分析 Vue 的实例属性和方法,接下来我们分析 Vue 的静态属性和方法。
我们再回到 initGlobalAPI 定义执行的地方,如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config // Vue.config 获取 config 全局变量
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => { // 设置Vue.config时直接报错,即不允许设置Vue.config值
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
// 通过ES5的defineProperty设置Vue的config的访问器属性
// 获取Vue.config时会执行configDef.get函数
// 设置Vue.config时会执行configDef.set函数
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
// exposed util methods.
// NOTE: these are not considered part of the public API - avoid relying on
// them unless you are aware of the risk.
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
// 2.6 explicit observable API
Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
initUse(Vue)
initMixin(Vue)
initExtend(Vue)
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# 2. 静态属性和方法
initGlobalAPI 方法的作用就是给初始化全局 API 即给 Vue 构造函数添加静态属性和方法,下面我们逐一分析。
# 2.1 config
initGlobalAPI 方法一开始就是添加全局配置,全局配置是一个静态只读属性。具体代码实现如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config // Vue.config 获取 config 全局变量
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => { // 设置Vue.config时直接报错,即不允许设置Vue.config值
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
// 通过ES5的defineProperty设置Vue的config的访问器属性
// 获取Vue.config时会执行configDef.get函数
// 设置Vue.config时会执行configDef.set函数
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
说明:关于全局配置我们在这里不做详细分析,后面都会讲解到,请移步到这里 (opens new window)学习。
# 2.2 util
接下来是给 Vue 添加 util 静态属性对象,包括 warn、extend、mergeOptions、defineReactive 四个属性。代码如下:
源码目录: `src/core/global-api/index.js`
// exposed util methods.
// NOTE: these are not considered part of the public API - avoid relying on
// them unless you are aware of the risk.
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 2.3 set
然后给 Vue 添加 set 静态方法,主要作用是向响应式对象中添加一个属性,并确保这个新属性同样是响应式的,且触发视图更新。代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
Vue.set = set
# 2.4 delete
接着给 Vue 添加 delete 静态方法,主要作用是删除对象的属性。如果对象是响应式的,确保删除能触发更新视图。这个方法主要用于避开 Vue 不能检测到属性被删除的限制,但是你应该很少会使用它。代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
Vue.delete = del
# 2.5 nextTick
然后给 Vue 添加 nextTick 静态方法,主要作用是在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调。在修改数据之后立即使用这个方法,获取更新后的 DOM。代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
# 2.6 observable
接下来给 Vue 添加 observable 静态属性,主要作用是让一个对象可响应。Vue 内部会用它来处理 data 函数返回的对象。代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => {
observe(obj)
return obj
}
2
3
4
说明:关于 observable 具体用法,请移步到这里 (opens new window)学习。
# 2.7 options
继续执行代码,给 Vue 添加 options 静态属性。这里要注意的是 Vue.options,现在它还只是一个空的对象,通过 Object.create(null) 创建。
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
接下来是给 options 添加属性,通过遍历 ASSET_TYPES 添加属性,首先我们看一下 ASSET_TYPES 定义,如下:
源码目录: src/shared/constants.js
export const ASSET_TYPES = [
'component',
'directive',
'filter'
]
2
3
4
5
执行完循环,options 就不是一个空对象了,如下:
Vue.options = {
components: Object.create(null),
directives: Object.create(null),
filters: Object.create(null),
_base: Vue
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 3. extend函数
接下来执行如下代码:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/index.js
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
extend 的作用是将 builtInComponents 的属性混合到 Vue.options.components 中,其中 builtInComponents 的定义如下:
源码目录: src/core/components/index.js
import KeepAlive from './keep-alive'
export default {
KeepAlive
}
2
3
4
5
从源码我们分析可以得出 builtInComponents 就是 Vue 内置组件 KeepAlive,所以最终合并后的结果为,如下:
Vue.options = {
components: {
KeepAlive
},
directives: Object.create(null),
filters: Object.create(null),
_base: Vue
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
说明:关于 extend 方法这里不做详细分析,后面会详细分析。
# 4. initUse
我们先从 initUse 的定义入手,代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/use.js
export function initUse (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) { /* */ }
}
2
3
该方法的作用是在 Vue 构造函数上添加 use 静态方法,也就是 Vue.use 这个全局API,这个方法的作用是安装 Vue.js 插件。如果插件是一个对象,必须提供 install 方法。如果插件是一个函数,它会被作为 install 方法。install 方法调用时,会将Vue 作为参数传入。
说明:关于 use 方法如何实现的这里不做详细分析,后面会详细分析。
提示:关于 use 的使用可以移步到这里 (opens new window)学习。
# 5. initMixin
接下来我们看一下 initMixin 的定义入手,代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/mixin.js
export function initMixin (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.mixin = function (mixin: Object) { /* */ }
}
2
3
initMixin 方法的作用是,在 Vue 上添加 mixin 静态方法,这个方法的作用是全局注册一个混入,影响注册之后所有创建的每个 Vue 实例。插件作者可以使用混入,向组件注入自定义的行为。不推荐在应用代码中使用。
说明:关于 mixin 方法如何实现的这里不做详细分析,后面会详细分析。
提示:关于 use 的使用可以移步到这里 (opens new window)学习。
# 6. initExtend
接着我们看一下 initExtend 的定义,代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/extend.js
export function initExtend (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Each instance constructor, including Vue, has a unique
* cid. This enables us to create wrapped "child
* constructors" for prototypal inheritance and cache them.
*/
Vue.cid = 0
/**
* Class inheritance
*/
Vue.extend = function (extendOptions: Object): Function { /* */ }
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
initExtend 方法在 Vue 上添加了 Vue.cid 静态属性,和 Vue.extend 静态方法。Vue.extend 这个方法的作用是使用基础 Vue 构造器,创建一个“子类”。参数是一个包含组件选项的对象。
说明:关于 use 方法如何实现的这里不做详细分析,后面会详细分析。
提示:关于 use 的使用可以移步到这里 (opens new window)学习。
# 7. initAssetRegisters
最后我们来看 initAssetRegisters 的定义,代码如下:
源码目录: src/core/global-api/assets.js
export function initAssetRegisters (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
/**
* Create asset registration methods.
*/
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue[type] = function (
id: string,
definition: Function | Object
): Function | Object | void { /* */ }
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
同 options 添加属性一样,通过遍历 ASSET_TYPES 给 Vue 添加 component ,directive,filter 三个静态方法。他们的作用分别为:
component:注册或获取全局组件。注册还会自动使用给定的id设置组件的名称。directive:注册或获取全局指令。filter:注册或获取全局过滤器。
提示:关于这三个的使用可以移步到component (opens new window)、directive (opens new window)、filter (opens new window)学习。
# 8. 其他
我们再回到 initGlobalAPI 函数执行的地方,如下:
源码目录: src/core/index.js
initGlobalAPI(Vue)
// expose FunctionalRenderContext for ssr runtime helper installation
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'FunctionalRenderContext', {
value: FunctionalRenderContext
})
2
3
4
5
6
执行完 initGlobalAPI 函数,接着又在 Vue 构造函数上定义了 FunctionalRenderContext 静态属性,是为了在 ssr 中使用它。
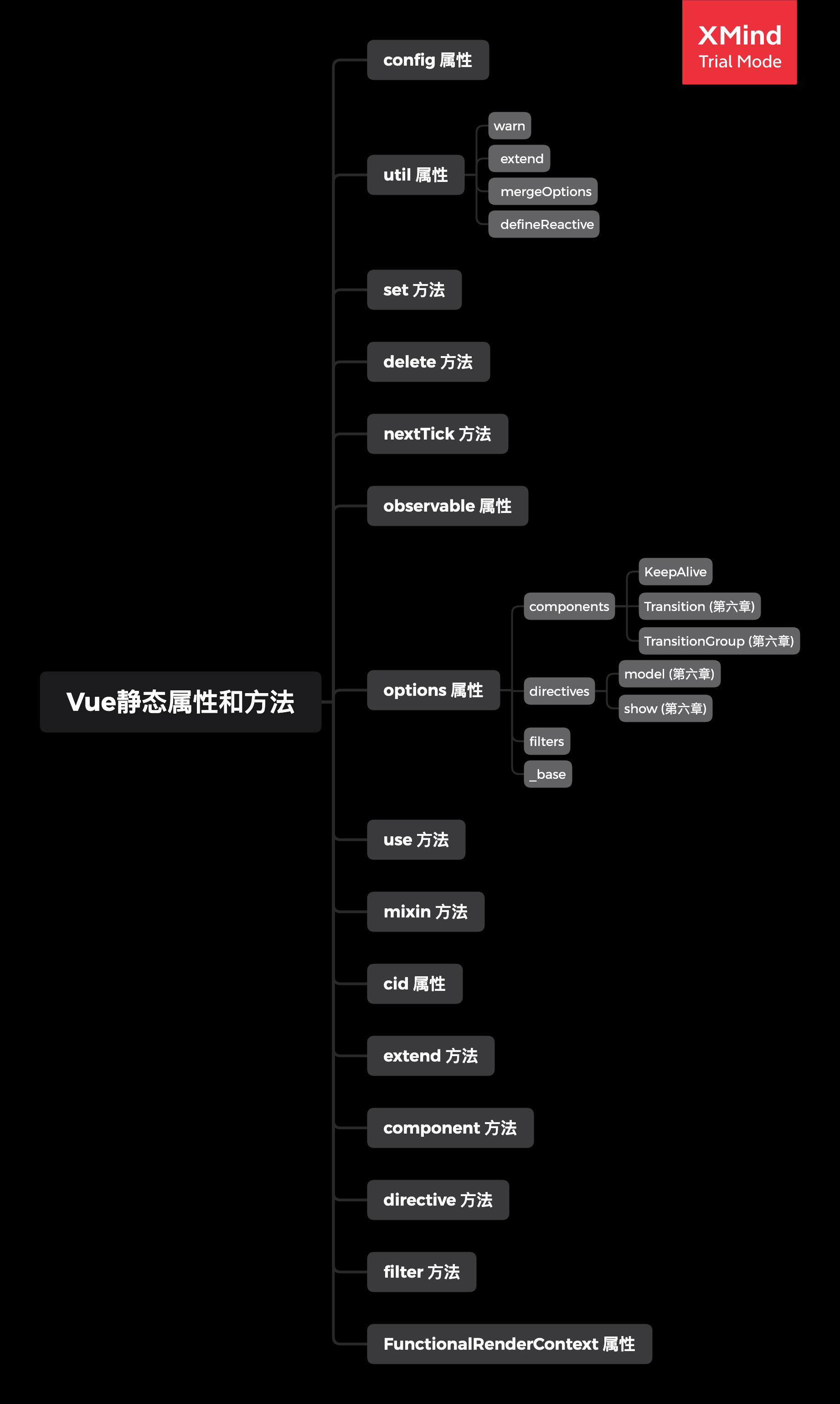
# 9. 总结
通过我们上面的分析,我们可以总结出 Vue 静态属性和方法即 Vue 全局 API,接下来我们已思维导图的方式总结。
说明:在本章节中没有遇到的 Vue 全局 API 我们也会在以后的分析总归纳进来,会在思维导图中标在出来具体的章节。