vue源码分析(十四) 编译之codegen
# 1. 概述
我们知道编译总共有三个过程, 即parse、optimize和 codegen,前面几章我们已经分析了解析和优化两个过程,接下来我们分析编译的最后一个过程就是把优化后的 AST 树转换成可执行的代码,在分析前我们还是以一个 case 进行讲解。
案例如下:
<ul :class="classObject" class="list" v-if="isShow">
<li v-for="(l, i) in list" :key="i" ref="i" @click="clickItem(index)">{{ i }}:{{ l }}</li>
</ul>
2
3
这段模板经过解析和优化两个过程生成的 AST 树如下:
{
attrsList: [],
attrsMap: {:class: "classObject", class: "list", v-if: "isShow"},
children: [
{
alias: "l",
attrsList: [ {name: "@click", value: "clickItem(index)", start: 109, end: 134}],
attrsMap: {v-for: "(l, i) in list", :key: "i", ref: "i", @click: "clickItem(index)"},
children: [
{
end: 150,
expression: "_s(i)+":"+_s(l)",
start: 135,
static: false,
text: "{{ i }}:{{ l }}",
tokens: (3) [{@binding: "i"}, ":", {@binding: "l"}],
type: 2
}
],
end: 155,
events: {click: {value: "clickItem(index)", dynamic: false, start: 109, end: 134}},
for: "list",
hasBindings: true,
iterator1: "i",
key: "i",
parent: {/* 省略... ul */},
plain: false,
rawAttrsMap: {
:key: {name: ":key", value: "i", start: 92, end: 100},
@click: {name: "@click", value: "clickItem(index)", start: 109, end: 134},
ref: {name: "ref", value: "i", start: 101, end: 108},
v-for: {name: "v-for", value: "(l, i) in list", start: 69, end: 91},
},
ref: ""i"",
refInFor: true,
start: 65,
static: false,
staticRoot: false,
tag: "li",
type: 1
}
],
classBinding: "classObject",
end: 171,
if: "isShow",
ifConditions: [
{
exp: "isShow",
block: {
attrsList: [],
attrsMap: {:class: "classObject", class: "list", v-if: "isShow"},
children: [/* 省略... li */],
classBinding: "classObject",
end: 171,
if: "isShow",
ifConditions: [/* 省略... ul */],
parent: undefined,
plain: false,
rawAttrsMap: {
:class: {name: ":class", value: "classObject", start: 4, end: 24},
class: {name: "class", value: "list", start: 25, end: 37},
v-if: {name: "v-if", value: "isShow", start: 38, end: 51}
},
start: 0,
static: false,
staticClass: ""list"",
staticRoot: false,
tag: "ul",
type: 1
}
}
],
parent: undefined,
plain: false,
rawAttrsMap: {
:class: {name: ":class", value: "classObject", start: 4, end: 24},
class: {name: "class", value: "list", start: 25, end: 37},
v-if: {name: "v-if", value: "isShow", start: 38, end: 51
},
start: 0,
static: false,
staticClass: ""list"",
staticRoot: false,
tag: "ul",
type: 1
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
接下来我们就看 vue 是如何将这样的一个 AST 树生成一个 render 函数代码的。
# 2. generate
我们在 vue源码分析(八) 编译之整体流程 (opens new window) 中分析过了编译的三个过程,即解析模板字符串生成 AST、优化语法树、生成代码,生成代码的过程是通过调用 generate 函数实现的,我们先来看一下它的定义,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
export function generate (
ast: ASTElement | void,
options: CompilerOptions
): CodegenResult {
const state = new CodegenState(options)
const code = ast ? genElement(ast, state) : '_c("div")'
return {
render: `with(this){return ${code}}`,
staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
从上面的源码我们可以知道,generate 首先通过 new 创建一个 CodegenState 实例,接着通过 genElement 将 ast 对象转换为字符串。
接下来我们分别来分析这两个过程。
# 3. CodegenState
首先我们看一下 CodegenState 的定义,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
export class CodegenState {
options: CompilerOptions;
warn: Function;
transforms: Array<TransformFunction>;
dataGenFns: Array<DataGenFunction>;
directives: { [key: string]: DirectiveFunction };
maybeComponent: (el: ASTElement) => boolean;
onceId: number;
staticRenderFns: Array<string>;
pre: boolean;
constructor (options: CompilerOptions) {
this.options = options
this.warn = options.warn || baseWarn
this.transforms = pluckModuleFunction(options.modules, 'transformCode')
this.dataGenFns = pluckModuleFunction(options.modules, 'genData')
this.directives = extend(extend({}, baseDirectives), options.directives)
const isReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no
this.maybeComponent = (el: ASTElement) => !!el.component || !isReservedTag(el.tag)
this.onceId = 0
this.staticRenderFns = []
this.pre = false
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
CodegenState 是根据 options 创建的对象,这里的 options 的值为,如下:
{
comments: true,
delimiters: undefined,
outputSourceRange: true,
shouldDecodeNewlines: false,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref: false,
warn: (msg, range, tip) {/*...*/}
__proto__: {
canBeLeftOpenTag: (val) {/*...*/},
directives: {
html: html(el, dir) {/*...*/},
model: model( el, dir, _warn ) {/*...*/},
text: text(el, dir) {/*...*/}
},
expectHTML: true,
getTagNamespace: getTagNamespace(tag) {/*...*/},
isPreTag: (tag) {/*...*/},
isReservedTag: (tag) {/*...*/},
isUnaryTag: (val) {/*...*/},
modules: (3) [
{
genData: genData(el) {/*...*/},
staticKeys: ["staticClass"],
transformNode: transformNode(el, options) {/*...*/}
}, {
genData: genData$1(el) {/*...*/},
staticKeys: ["staticStyle"],
transformNode: transformNode$1(el, options) {/*...*/}
}, {
preTransformNode: preTransformNode(el, options) {/*...*/}
}
],
mustUseProp: (tag, type, attr) {/*...*/},
staticKeys: "staticClass,staticStyle"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
所以根据 options 通过 new 创建的对象实例为,如下:
{
dataGenFns: [
genData() {/*...*/},
genData$() {/*...*/}
],
directives: {
bind: bind$1(el, dir) {/*...*/},
cloak: noop(a, b, c) {/*...*/},
html: html(el, dir) {/*...*/},
model: model( el, dir, _warn ) {/*...*/},
on: on(el, dir) {/*...*/},
text: text(el, dir) {/*...*/}
},
maybeComponent: ƒ (el) {/*...*/},
onceId: 0,
options: {/* 省略... */}, // 同上
pre: false,
staticRenderFns: [],
transforms: [],
warn: warn(msg, range, tip) {/*...*/}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
接下来我们分一下 CodegenState 实例的每个属性的作用:
options: 缓存实例化传递进来的optionswarn: 用来打印警告信息的transforms: 空数组dataGenFns: 对静态类和静态样式的处理directives: 对指令的相关操作isReservedTag: 保留标签标志maybeComponent: 判断是组件onceId: 使用v-once的递增idstaticRenderFns: 对静态根节点的处理pre:v-pre标识
注意:关于 pluckModuleFunction 和 options.modules 我们在 vue源码分析(十一) 编译之解析(parse)——parse (opens new window) 中已经分析过了。
# 4. 整体流程
我们先以上面的案例来分析,代码生成的整个流程,通过分析 generate我们知道代码生成是通过 genElement 函数将 ast 对象转换为字符串,接下来我们从 genElement 函数来开始分析。
# 4.1 genElement
我们首先看一下 genElement 的定义,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
/**
* 将ast对象转换为字符串
* @param {ast树} el
* @param {CodegenState 实例} state
*/
export function genElement (el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string {
if (el.parent) {
el.pre = el.pre || el.parent.pre
}
// 对一些标签属性的处理
// 处理静态树节点
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
// 处理 v-once 节点
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
// 处理 v-for 节点
return genFor(el, state)
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
// 处理 v-if 节点
return genIf(el, state)
} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {
// 处理 template 节点
return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'
} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
// 处理 slot 节点
return genSlot(el, state)
} else {
// component or element
// 处理组件 或 元素节点
let code
if (el.component) {
// 处理组件节点
code = genComponent(el.component, el, state)
} else {
//核心的body部分
let data
if (!el.plain || (el.pre && state.maybeComponent(el))) {
// 1、生成节点的数据对象data的字符串
data = genData(el, state)
}
// 2、查找其子节点,生成子节点的字符串
const children = el.inlineTemplate ? null : genChildren(el, state, true)
// 3、将tag,data,children拼装成字符串
code = `_c('${el.tag}'${
data ? `,${data}` : '' // data
}${
children ? `,${children}` : '' // children
})`
}
// module transforms
// 循环执行 state.transforms 数组中的 genData 函数
for (let i = 0; i < state.transforms.length; i++) {
code = state.transforms[i](el, code)
}
return code
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
我们案例中跟节点为 ul ,属性有:class: "classObject"、 class: "list"、 v-if: "isShow" 所以代码会执行到 genIf 如下语句:
return genIf(el, state)
# 4.2 genIf
接下来我们看看 genIf 的定义,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
export function genIf (
el: any,
state: CodegenState,
altGen?: Function,
altEmpty?: string
): string {
el.ifProcessed = true // avoid recursion
return genIfConditions(el.ifConditions.slice(), state, altGen, altEmpty)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
genIf 的逻辑很简单,主要是通过执行 genIfConditions ,处理 v-if/v-else-if/v-else 指令所对应的 AST 节点。
# 4.3 genIfConditions
接下来我们看看 genIfConditions 的逻辑,首先是判断 AST 树的 conditions 数组是否有值,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
function genIfConditions (
conditions: ASTIfConditions,
state: CodegenState,
altGen?: Function,
altEmpty?: string
): string {
if (!conditions.length) {
return altEmpty || '_e()'
}
/* 省略... */
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
我们通过源码可以知道如果 conditions 数组为空,则返回一个生成空的虚拟 dom 的函数字符串;如果conditions 数组不为空,代码继续往下执行,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
const condition = conditions.shift()
if (condition.exp) {
return `(${condition.exp})?${
genTernaryExp(condition.block)
}:${
genIfConditions(conditions, state, altGen, altEmpty)
}`
} else {
return `${genTernaryExp(condition.block)}`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
当 conditions 数组不为空时,首先取第一个元素赋值给变量 condition,在我们当前案例中,我们知道 conditions 为:
[
{
exp: "isShow",
block: {/* 省略,ul节点生成的AST树 */}
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
所以接下来的 if 条件 condition.exp 为 true 继续执行 if 语句块,而此处的 else 语句块是 conditions 中 v-else 对应的 AST 树执行的逻辑,在我们当前案例中不会执行else 语句块。
if 语句块的作用是调用 genIfConditions 进行递归生成二元表达式。我们从源码可以得到二元表达式的条件为 condition.exp 第一个表达式为 genTernaryExp(condition.block) 第二个表达式为 genIfConditions(conditions, state, altGen, altEmpty),我们接下来看看 genTernaryExp 的定义如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// v-if with v-once should generate code like (a)?_m(0):_m(1)
function genTernaryExp (el) {
return altGen
? altGen(el, state)
: el.once
? genOnce(el, state)
: genElement(el, state)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
genTernaryExp 函数里面主要是一个多元的表达式,首先判断 altGen 如果存在,则返回调用altGen(el, state) 执行的结果,如果不存在接着判断当前 AST 树是否使用了 v-once 指令即判断 el.once 属性是否存在,如果存在则返回调用genOnce(el, state) 执行的结果,即返回一个创建静态标签节点的函数的字符,如果不存在则继续回调 genElement(el, state) 生成节点的字符串。
在我们当前案例中,会执行 genElement(el, state) 。genElement 我们前面已经分析过了,这次执行 genElement 时,由于我们在 genIf 给 AST 树添加了 el.ifProcessed = true ,所以这次执行 genElement 将不会在执行到 genIf 对应的 if 语句块,而是 执行 else 语句,我们再来回顾一下 genElement 的 else 语句块,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// component or element
let code
if (el.component) {
code = genComponent(el.component, el, state)
} else {
let data
if (!el.plain || (el.pre && state.maybeComponent(el))) {
data = genData(el, state)
}
const children = el.inlineTemplate ? null : genChildren(el, state, true)
code = `_c('${el.tag}'${
data ? `,${data}` : '' // data
}${
children ? `,${children}` : '' // children
})`
}
// module transforms
for (let i = 0; i < state.transforms.length; i++) {
code = state.transforms[i](el, code)
}
return code
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
从源码我们可以知道 else 语句块主要是对组件和元素进行处理生成 render 表达式字符串。
这段代码首先定义一个变量 code 用来保存最终生成 render 表达式字符串,接下来是一个 if...else 语句块,其中 if 语句块只要是对组件的处理,else 语句块是对普通元素的处理,在我们这个案例中会执行到else 语句块,首先会判断当前标签是不否存在 plain 属性或者存在 pre属性并且是组件,则会执行 if 语句,此时我们 AST 树没有 plain 属性,所以会调用 genData 函数生成节点的数据对象 data 的字符串。
接下来通过判断标签是不是内联模板则返回 null ,如果不是内联模板则直接调用 genChildren,查找其子节点,生成子节点的字符串。
接着将 tag,data,children 拼装成字符串,赋值给 code。
最后通过循环 state.transforms 数组,执行数组中的每个函数,我们在前面分析此案例生成的 AST 树的时候知道 state.transforms 是通过 this.transforms = pluckModuleFunction(options.modules, 'transformCode') 这句生成的,此时的 state.transforms 为空,所以不会执行循环里面的代码,最后直接返回 code。
说明:关于 el.plain 我们在 vue源码分析(十二) 编译之解析(parse)——处理标签 (opens new window) 中已经做了详细的分析。
关于内联模板 inline-template ,可以查看 这里 (opens new window) 。
关于 pluckModuleFunction 可以查看 这里 (opens new window)
说明:关于 genData、genChildren 我们会在下面小节中做详细的分析。
# 4.4 genData
接下我们看看 genData 的代码逻辑,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
export function genData (el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string {
let data = '{'
// directives first.
// directives may mutate the el's other properties before they are generated.
const dirs = genDirectives(el, state)
if (dirs) data += dirs + ','
/* 省略... */
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
genData 首先是定义一个 data 变量,用来存储生成节点的数据对象 data 的字符串,接下来调用 genDirectives 对 directives 进行处理将指令对象转换成一个字符串格式,例如 <div v-info></div> 则变成 directives:[{name:"info",rawName:"v-info"}]。
接下来判断获取到的指令字符串是否存在,如果存在则将获取的字符串追加到 data 变量并且已逗号结尾,如果不存在直接执行后续的代码。
说明:关于 genDirectives 我们会在下面小节中做详细的分析。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// key
if (el.key) {
data += `key:${el.key},`
}
// ref
if (el.ref) {
data += `ref:${el.ref},`
}
if (el.refInFor) {
data += `refInFor:true,`
}
// pre
if (el.pre) {
data += `pre:true,`
}
// record original tag name for components using "is" attribute
if (el.component) {
data += `tag:"${el.tag}",`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
这段代码就是对一些属性的操作,key,ref,refInFor,pre,tag 纯粹将他们拼接起来,在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这些属性值都是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// module data generation functions
for (let i = 0; i < state.dataGenFns.length; i++) {
data += state.dataGenFns[i](el)
}
2
3
4
我们在前面的章节中分析知道 pluckModuleFunction 实际上就是获取所有 modules 中的 genDatas 函数,其中, class module 和 style module定义了 genDatas 函数。
下面我们看看这两个 genDatas 函数。
源码目录:src/platforms/web/compiler/modules/class.js
function genData (el: ASTElement): string {
let data = ''
if (el.staticClass) {
data += `staticClass:${el.staticClass},`
}
if (el.classBinding) {
data += `class:${el.classBinding},`
}
return data
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
源码目录:src/platforms/web/compiler/modules/style.js
function genData (el: ASTElement): string {
let data = ''
if (el.staticStyle) {
data += `staticStyle:${el.staticStyle},`
}
if (el.styleBinding) {
data += `style:(${el.styleBinding}),`
}
return data
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这个函数的逻辑一样,就是对静态属性 class 、style 和动态属性 :class 、:style 的处理,把处理结果值拼接起来返回。
在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点定义了el.staticClass 和 el.classBinding ,因此最终生成的 data 字符串如下:
'staticClass:"list",class:classObject,'
我们再回到 genData 函数,继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// attributes
if (el.attrs) {
data += `attrs:${genProps(el.attrs)},`
}
// DOM props
if (el.props) {
data += `domProps:${genProps(el.props)},`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
这段代码是对普通属性和 props 属性进行处理,将结果追加到 data 变量并且已逗号结尾。同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这些属性值都是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,接下来的代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// event handlers
if (el.events) {
data += `${genHandlers(el.events, false)},`
}
if (el.nativeEvents) {
data += `${genHandlers(el.nativeEvents, true)},`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
这段代码是对原生事件和自定义事件进行处理,将结果追加到 data 变量并且已逗号结尾。同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这些属性值都是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// slot target
// only for non-scoped slots
if (el.slotTarget && !el.slotScope) {
data += `slot:${el.slotTarget},`
}
// scoped slots
if (el.scopedSlots) {
data += `${genScopedSlots(el, el.scopedSlots, state)},`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
这段代码是对非作用域插槽和作用于插槽进行处理,将结果追加到 data 变量并且已逗号结尾。同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这些属性值都是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// component v-model
if (el.model) {
data += `model:{value:${
el.model.value
},callback:${
el.model.callback
},expression:${
el.model.expression
}},`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这段代码是在组件上使用 v-model 指令的情况,对 AST 树的 model 属性进行处理,将结果追加到 data 变量并且已逗号结尾。
例如:v-model = "name",则转换的 AST 树为:
{
callback: "function ($$v) {name=$$v}",
expression: ""name"",
value: "(name)"
}
2
3
4
5
所有最终生成的字符串为,如下:
'model:{value:(name),callback:function ($$v) {name=$$v},expression:"name"},'
同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这些属性值都是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// inline-template
if (el.inlineTemplate) {
const inlineTemplate = genInlineTemplate(el, state)
if (inlineTemplate) {
data += `${inlineTemplate},`
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
这段代码是对内联模板的处理,将结果追加到 data 变量并且已逗号结尾。同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这个属性值是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
data = data.replace(/,$/, '') + '}'
// v-bind dynamic argument wrap
// v-bind with dynamic arguments must be applied using the same v-bind object
// merge helper so that class/style/mustUseProp attrs are handled correctly.
if (el.dynamicAttrs) {
data = `_b(${data},"${el.tag}",${genProps(el.dynamicAttrs)})`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
这段代码首先通过 replace 替换,将最后一个逗号替换成空字符,并且在 data 字符串末尾添加一个 } 括号,接着判断AST 树是否存在动态属性,例如:
<!-- 动态参数的缩写 (2.6.0+) -->
<div :[key]="name"> ... </div>
2
转换的 AST 树为:
dynamicAttrs: [{
dynamic: true,
end: 17,
name: "key",
start: 5,
value: "name"
}]
2
3
4
5
6
7
如果存在动态参数的属性,最终通过 genProps 处理,,将结果和 data 变量合并,如下:
'_b({staticClass:"list",class:classObject},"ul",_d({},[val,name]))'
同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这个属性值是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
我们继续往下看,代码如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// v-bind data wrap
if (el.wrapData) {
data = el.wrapData(data)
}
// v-on data wrap
if (el.wrapListeners) {
data = el.wrapListeners(data)
}
return data
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
genData 最后这两个 if 语句是对包装数据和包装事件进行处理,例如:
<!-- 绑定一个全是 attribute 的对象 -->
<div v-bind="{ id: someProp, 'other-attr': otherProp }"></div>
<!-- 对象语法 (2.4.0+) -->
<button v-on="{ mousedown: doThis, mouseup: doThat }"></button>
2
3
4
5
同样在我们的例子中, ul AST 元素节点这些属性值都是 undefined ,所以不会执行 if 中的语句 。
至此我们把 genData 的业务逻辑已经分析完了,最后我们总结一下,genData的主要作用:
- 通过
genDirectives对指令进行处理 - 对一些属性的处理,包括
key,ref,refInFor,pre,tag,纯粹将他们拼接起来 - 对静态属性
class、style和动态属性:class、:style的处理 - 通过
genProps对attrs和props属性进行处理 - 通过
genHandlers对自定义事件和原生事件进行处理 - 对
slot进行处理和通过genScopedSlots对作用于插槽进行处理 - 对些属性
v-model的处理 - 通过
genInlineTemplate内联模板inline-template进行处理 - 对动态属性处理
v-bind绑定的包装数据处理v-on绑定的包装事件处理
# 4.5 genChildren
我们再回到 genElement 中的 else 语句块,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
// component or element
let data
if (!el.plain || (el.pre && state.maybeComponent(el))) {
data = genData(el, state)
}
const children = el.inlineTemplate ? null : genChildren(el, state, true)
code = `_c('${el.tag}'${
data ? `,${data}` : '' // data
}${
children ? `,${children}` : '' // children
})`
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
前面分析过了 genData ,接下通过判断内联模板是否存在,如果存在则 children 为空, 如果不存在则 children 为 genChildren(el, state, true) ,在我们当前案例中内联模板不存在所以执行 genChildren ,我们来看看 genChildren 的代码逻辑,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
export function genChildren (
el: ASTElement,
state: CodegenState,
checkSkip?: boolean,
altGenElement?: Function,
altGenNode?: Function
): string | void {
const children = el.children
if (children.length) {
const el: any = children[0]
// optimize single v-for
if (children.length === 1 &&
el.for &&
el.tag !== 'template' &&
el.tag !== 'slot'
) {
const normalizationType = checkSkip
? state.maybeComponent(el) ? `,1` : `,0`
: ``
return `${(altGenElement || genElement)(el, state)}${normalizationType}`
}
const normalizationType = checkSkip
? getNormalizationType(children, state.maybeComponent)
: 0
const gen = altGenNode || genNode
return `[${children.map(c => gen(c, state)).join(',')}]${
normalizationType ? `,${normalizationType}` : ''
}`
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
genChildren 首先获取子节点 AST 树赋值给 children,接下来判断 children 数组是否有值,如果有值,则继续执行下面逻辑:
- 对
v-for进行简单优化 - 对其他子节点进行处理
在们当前的案例中,此时的 children 为 li AST 树,因为 li AST 元素节点是 ul AST 元素节点的 children 之一,满足 children.length === 1 && el.for && el.tag !== 'template' && el.tag !== 'slot' 条件,if 语句中先判断 checkSkip,如果为 false,normalizationType = '', 如果为 true,再判断是不是组件,如果是则 normalizationType = ',1', 否则 normalizationType = ',0',最后返回 genElement 生成 li AST 元素节点的代码并拼接 normalizationType 的值。
再回到了我们之前分析的 genElement 函数。此时会执行到下面的逻辑,如下:
// 如果为 true,在判断是不是组件,如果是则 normalizationType = ',1', 否则 normalizationType = ',0' 因此通过 genElement 生成 li AST 元素节点的代码,也就回到了我们之前分析的 genElement 函数。此时会执行到下面的逻辑,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
return genFor(el, state)
这里我们对 genFor 不多做分析,后面单独分析,我们只要知道 genFor 是对 AST 元素节点中和 for 相关的一些属性的处理,然后再次调用 genElement 生成 li AST 元素节点的代码并拼接一些 for 相关的属性,最后返回这个拼接后的代码字符串。
再次执行 genElement 函数的时候,由于在 genFor 中标记了已处理的标记,即 el.forProcessed = true ,所以这次执行 genElement 将不会在执行到 genFor 对应的 if 语句块,而是执行 else 语句。else 语句我们前面已经分析过了,此时又会执行 else 语句中的 genData 和 genChildren 函数,参数是 li AST 元素节点。
genData
genData 我们前面已经分析过了,这里需要强调一下,在处理 li AST 元素节点时,会执行下面的几个逻辑语句,如下:
// key
if (el.key) {
data += "key:" + (el.key) + ",";
}
// ref
if (el.ref) {
// 保存ref到data属性上
data += "ref:" + (el.ref) + ",";
}
if (el.refInFor) {
// 保存refInFor到data属性上
data += "refInFor:true,";
}
// module data generation functions
for (var i = 0; i < state.dataGenFns.length; i++) {
data += state.dataGenFns[i](el);
}
// event handlers
if (el.events) {
data += (genHandlers(el.events, false)) + ",";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
这段代码中除了 genHandlers 逻辑我们没有分析,其他逻辑前面都分析过了这里就不重复讲解了。
最后通过 genData 生成的li AST 元素节点的代码字符串,如下:
data = '{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}}'
genChildren
我们继续看看 genChildren 对li AST 元素节点的处理,这次执行 genChildren 获取到的子节点 AST 树为,如下:
[
{
"type": 2,
"expression": "_s(i)+\":\"+_s(l)",
"tokens": [
{
"@binding": "i"
},
":",
{
"@binding": "l"
}
],
"text": "{{ i }}:{{ l }}",
"start": 135,
"end": 150,
"static": false
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
子节点 AST 树为文本节点,所以不会执行 if 语句而是执行一下代码,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
const normalizationType = checkSkip
? getNormalizationType(children, state.maybeComponent)
: 0
const gen = altGenNode || genNode
return `[${children.map(c => gen(c, state)).join(',')}]${
normalizationType ? `,${normalizationType}` : ''
}`
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
首先通过 checkSkip 值来判断 normalizationType(规范化类型) 值的来源,在我们当前案例中,checkSkip 为 true ,所以会执行 getNormalizationType 函数,定义如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
function getNormalizationType (
children: Array<ASTNode>,
maybeComponent: (el: ASTElement) => boolean
): number {
let res = 0
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
const el: ASTNode = children[i]
if (el.type !== 1) {
continue
}
if (needsNormalization(el) ||
(el.ifConditions && el.ifConditions.some(c => needsNormalization(c.block)))) {
res = 2
break
}
if (maybeComponent(el) ||
(el.ifConditions && el.ifConditions.some(c => maybeComponent(c.block)))) {
res = 1
}
}
return res
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
我们通过注视知道 getNormalizationType 的作用是确定子数组所需的规范化,规范化类型有一下三种:
0: 不需要规范化1: 需要简单的规范化(可能是1级深嵌套数组)2: 需要完全规范化
我们再来看看 getNormalizationType 的执行逻辑,首先循环子节点,获取的每个子节点。
然后第一个if 语句判断节点类型,如果节点类型为 1,则跳出本次循环,如果节点类型不为 1,则继续往下执行。
接下来第二个if 语句块是对需要简单的规范化(可能是1级深嵌套数组)的节点的逻辑处理,将 res 赋值为 2,需要满足以下条件才会执行,if 语句块:
- 通过
needsNormalization来判断节点上有v-for或标签名是template或slot - 或者节点是
if块,并且块内元素有自定义组件的
第三个if 语句块是对需要完全规范化的节点的逻辑处理,将 res 赋值为 1,需要满足以下条件才会执行,if 语句块:
el是自定义组件- 或者节点是
if块,并且块内元素有自定义组件的
我们再来看看 needsNormalization 的定义,如下:
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
function needsNormalization (el: ASTElement): boolean {
return el.for !== undefined || el.tag === 'template' || el.tag === 'slot'
}
2
3
needsNormalization 很简单就是判断节点是否需要规范化,即满足一下条件:
- 节点存在
for属性 - 或者节点标签是
template - 或者节点标签是
slot
在我们当前案例中,子节点类型为 2,所以在通过 getNormalizationType 获取规范化类型时,执行的是第一个if 语句,得到的 normalizationType 为 0。
我们回到 genChildren继续往下看,接下来是遍历子节点,调用 genNode 函数处理子节点。
genNode 方法,根据不同的 type 执行具体的方法。在我们的例子中,li AST 元素节点的 children 是type 为 2 的表达式 AST 元素节点,那么会执行到 genText(node) 逻辑,最后 genText 生成的字符串为:
"_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))"
li AST元素节点处理
我们再回到 genChildren 最后将遍历li AST 元素节点的子节点生成的字符串拼接起来,如下:
"[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))]"
我们再回到 genElement 中,在 else 语句li AST 元素节点生成的字符串 data,如下:
"{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}}"
然后拼接li AST 元素节点生成的字符串 data 和li AST 元素节点的子节点生成的字符串 children 赋值给变量 code,并返回 code,如下:
"_c('li',{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}},[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))])"
我们再回到 genFor 中,将节点的 for 属性的和 code 拼接起来,如下:
"_l((list),function(l,i){return _c('li',{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}},[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))])})"
至此li AST 元素节点处理生成的字符串已全部完成,接下来我们继续回到ul AST 元素节点的处理。
ul AST元素节点
我们再回到 genChildren ,这时处理的是ul AST 元素节点的子节点生成的字符串拼接起来,如下:
"_l((list),function(l,i){return _c('li',{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}},[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))])}),0"
我们再回到 genElement ,这时对ul AST 元素节点的处理生成的字符串 data ,如下:
"{staticClass:"list",class:classObject}"
生成的 children 字符串就是执行 genChildren 函数返回的结果,如上。
然后拼接ul AST 元素节点生成的字符串 data 和ul AST 元素节点的子节点生成的字符串 children 赋值给变量 code,并返回 code,如下:
"_c('ul',{staticClass:"list",class:classObject},_l((list),function(l,i){return _c('li',{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}},[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))])}),0)"
我们再回到 genIfConditions ,此函数中通过递归执行 genIfConditions 来处理 v-if 生成的 AST 树中对应的 ifConditions 数组中的所有节点,最终生成二元表达式,如下:
"(isShow)?_c('ul',{staticClass:"list",class:classObject},_l((list),function(l,i){return _c('li',{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}},[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))])}),0):_e()"
我们再回到 generate 函数,将 AST 树生成的代码字符串,拼接成一个 with 语句如下:
"with(this){return (isShow)?_c('ul',{staticClass:"list",class:classObject},_l((list),function(l,i){return _c('li',{key:i,ref:"i",refInFor:true,on:{"click":function($event){return clickItem(index)}}},[_v(_s(i)+":"+_s(l))])}),0):_e()}"
至此模板生成的 AST 元素节点处理生成的字符串已全部分析完成。
说明:关于 genFor、genHandlers 、genNode、genText,我们会在下一小节单独分析。
# 4.6 genFor
# 4.7 genHandlers
# 4.8 genNode
# 4.9 genText
# 4.10 总结
generate调用栈:
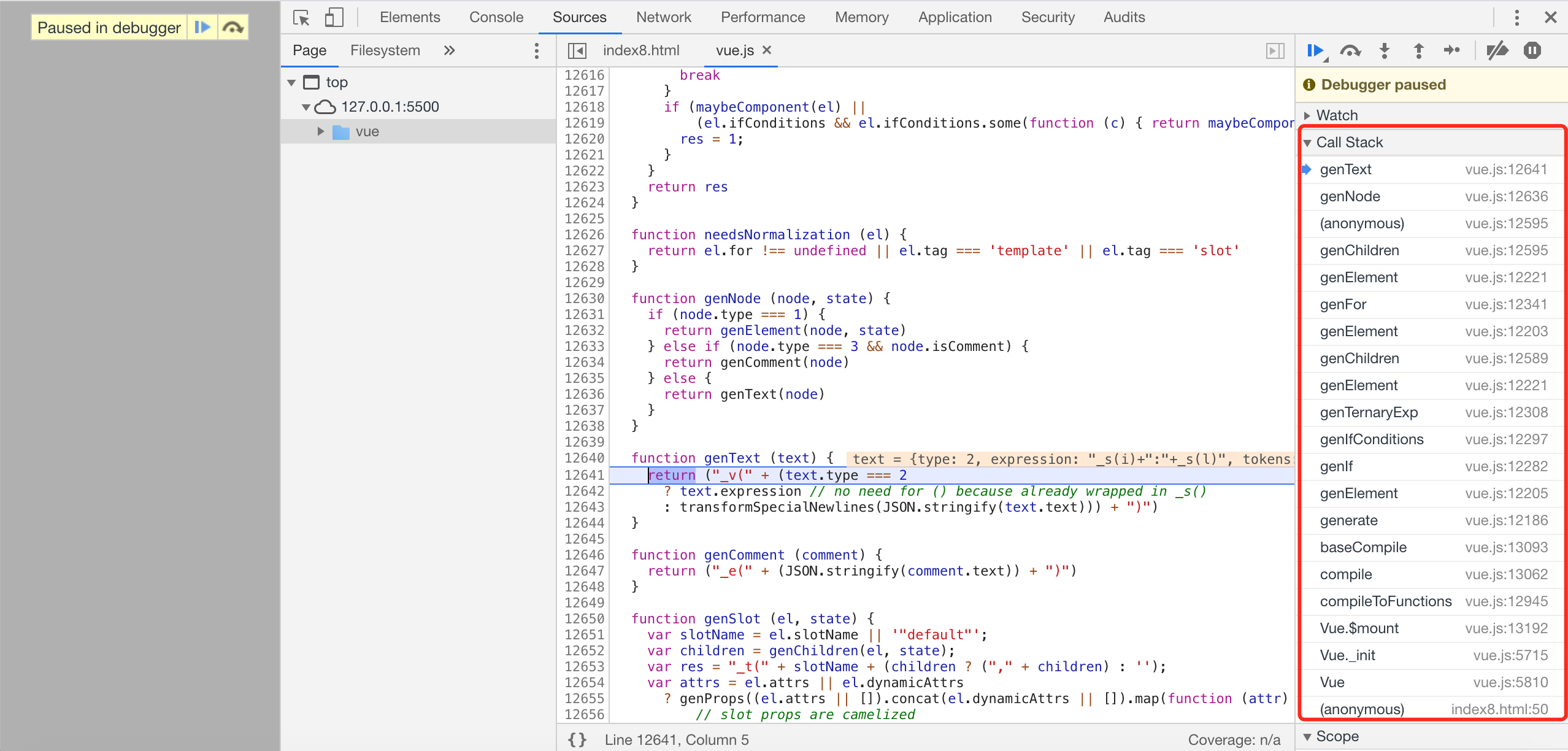
说明:关于 genDirectives 、genProps 、genScopedSlots、genInlineTemplate 在我们案例中没有执行到,我们会在后面单独分析。
# 5. 其他生成器
源码目录:src/compiler/codegen/index.js
# 5.1 genStatic
# 5.2 genOnce
# 5.3 genDirectives
说明:关于 directives 可以移步到 这里 (opens new window) 学习。
# 5.4 genProps
说明:关于 props 和 attrs 的区别可以移步到 这里 (opens new window) 学习。